Gift Tax Laws in Japan: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Japan’s Gift Tax Law?
Japan’s gift tax law imposes a tax on the transfer of property without adequate compensation. This includes gifts of money, real estate, and other assets. The tax is levied on the recipient of the gift, not the donor.
Who is Subject to Japan’s Gift Tax?
Anyone who receives a gift from a Japanese resident or a gift of Japanese property is subject to the gift tax. This includes both Japanese citizens and foreign nationals.
What is the Gift Tax Rate in Japan?
The gift tax rate in Japan varies depending on the relationship between the donor and the recipient. The rates are as follows:
- 10% for gifts between spouses
- 15% for gifts between lineal descendants (e.g., children, grandchildren)
- 20% for gifts between siblings
- 25% for gifts between other relatives
- 30% for gifts between non-relatives
What are the Gift Tax Exemptions in Japan?
There are a number of exemptions to the gift tax in Japan, including:
- Gifts of up to ¥1.1 million per year from a spouse
- Gifts of up to ¥500,000 per year from lineal descendants
- Gifts of up to ¥200,000 per year from siblings
- Gifts of up to ¥100,000 per year from other relatives
- Gifts of up to ¥50,000 per year from non-relatives
How to Calculate Gift Tax in Japan
To calculate the gift tax in Japan, you must first determine the taxable value of the gift. This is the fair market value of the gift on the date it was received. Once you have determined the taxable value, you can use the following formula to calculate the gift tax:
Gift tax = Taxable value x Gift tax rate
FAQs about Japan’s Gift Tax Law
- Q: What is the gift tax reporting deadline in Japan?
A: The gift tax return must be filed within 3 months of the date the gift was received. - Q: Can I avoid paying gift tax in Japan?
A: There are a number of ways to avoid paying gift tax in Japan, such as making gifts within the annual exemption limits or using a gift trust. - Q: What are the penalties for not paying gift tax in Japan?
A: The penalties for not paying gift tax in Japan can be severe, including fines and imprisonment.
Conclusion
Japan’s gift tax law is a complex topic. If you are planning to give or receive a gift in Japan, it is important to consult with a tax advisor to ensure that you comply with the law.
japan gift tax law
Gift Tax in Japan: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Japan’s Gift Tax?
Japan’s gift tax is a tax on the transfer of property without adequate compensation. This includes gifts of money, real estate, and other assets. The tax is levied on the recipient of the gift, not the donor.
Who is Subject to Japan’s Gift Tax?
Anyone who receives a gift from a Japanese resident or a gift of Japanese property is subject to the gift tax. This includes both Japanese citizens and foreign nationals.
What is the Gift Tax Rate in Japan?
The gift tax rate in Japan varies depending on the relationship between the donor and the recipient. The rates are as follows:
- 10% for gifts between spouses
- 15% for gifts between lineal descendants (e.g., children, grandchildren)
- 20% for gifts between siblings
- 25% for gifts between other relatives
- 30% for gifts between non-relatives
What are the Gift Tax Exemptions in Japan?
There are a number of exemptions to the gift tax in Japan, including:
- Gifts of up to ¥1.1 million per year from a spouse
- Gifts of up to ¥500,000 per year from lineal descendants
- Gifts of up to ¥200,000 per year from siblings
- Gifts of up to ¥100,000 per year from other relatives
- Gifts of up to ¥50,000 per year from non-relatives
How to Calculate Gift Tax in Japan
To calculate the gift tax in Japan, you must first determine the taxable value of the gift. This is the fair market value of the gift on the date it was received. Once you have determined the taxable value, you can use the following formula to calculate the gift tax:
Gift tax = Taxable value x Gift tax rate
Conclusion
Japan’s gift tax law is a complex topic. If you are planning to give or receive a gift in Japan, it is important to consult with a tax advisor to ensure that you comply with the law.
FAQs about Japan’s Gift Tax Law
- Q: What is the gift tax reporting deadline in Japan?
A: The gift tax return must be filed within 3 months of the date the gift was received. - Q: Can I avoid paying gift tax in Japan?
A: There are a number of ways to avoid paying gift tax in Japan, such as making gifts within the annual exemption limits or using a gift trust. - Q: What are the penalties for not paying gift tax in Japan?
A: The penalties for not paying gift tax in Japan can be severe, including fines and imprisonment.
gift tax japan spouse
Gift Tax in Japan: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Japan’s Gift Tax?
Japan’s gift tax is a tax on the transfer of property without adequate compensation. This includes gifts of money, real estate, and other assets. The tax is levied on the recipient of the gift, not the donor.
Who is Subject to Japan’s Gift Tax?
Anyone who receives a gift from a Japanese resident or a gift of Japanese property is subject to the gift tax. This includes both Japanese citizens and foreign nationals.
What is the Gift Tax Rate in Japan?
The gift tax rate in Japan varies depending on the relationship between the donor and the recipient. The rates are as follows:
- 10% for gifts between spouses
- 15% for gifts between lineal descendants (e.g., children, grandchildren)
- 20% for gifts between siblings
- 25% for gifts between other relatives
- 30% for gifts between non-relatives
What are the Gift Tax Exemptions in Japan?
There are a number of exemptions to the gift tax in Japan, including:
- Gifts of up to ¥1.1 million per year from a spouse
- Gifts of up to ¥500,000 per year from lineal descendants
- Gifts of up to ¥200,000 per year from siblings
- Gifts of up to ¥100,000 per year from other relatives
- Gifts of up to ¥50,000 per year from non-relatives
What is the Gift Tax Annual Exclusion for 2023, 2022, and 2024?
The gift tax annual exclusion is the amount of money that you can give to someone each year without having to pay gift tax. The annual exclusion for 2023, 2022, and 2024 is ¥1.1 million.
How to Calculate Gift Tax in Japan
To calculate the gift tax in Japan, you must first determine the taxable value of the gift. This is the fair market value of the gift on the date it was received. Once you have determined the taxable value, you can use the following formula to calculate the gift tax:
Gift tax = Taxable value x Gift tax rate
Conclusion
Japan’s gift tax law is a complex topic. If you are planning to give or receive a gift in Japan, it is important to consult with a tax advisor to ensure that you comply with the law.
FAQs about Japan’s Gift Tax Law
- Q: What is the gift tax reporting deadline in Japan?
A: The gift tax return must be filed within 3 months of the date the gift was received. - Q: Can I avoid paying gift tax in Japan?
A: There are a number of ways to avoid paying gift tax in Japan, such as making gifts within the annual exemption limits or using a gift trust. - Q: What are the penalties for not paying gift tax in Japan?
A: The penalties for not paying gift tax in Japan can be severe, including fines and imprisonment.
gift tax calculator japan
Gift Tax: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Gift Tax?
Gift tax is a tax on the transfer of property without adequate compensation. This includes gifts of money, real estate, and other assets. The tax is levied on the recipient of the gift, not the donor.
Who is Subject to Gift Tax?
Anyone who receives a gift from a U.S. citizen or resident or a gift of U.S. property is subject to the gift tax. This includes both U.S. citizens and foreign nationals.
What is the Gift Tax Rate?
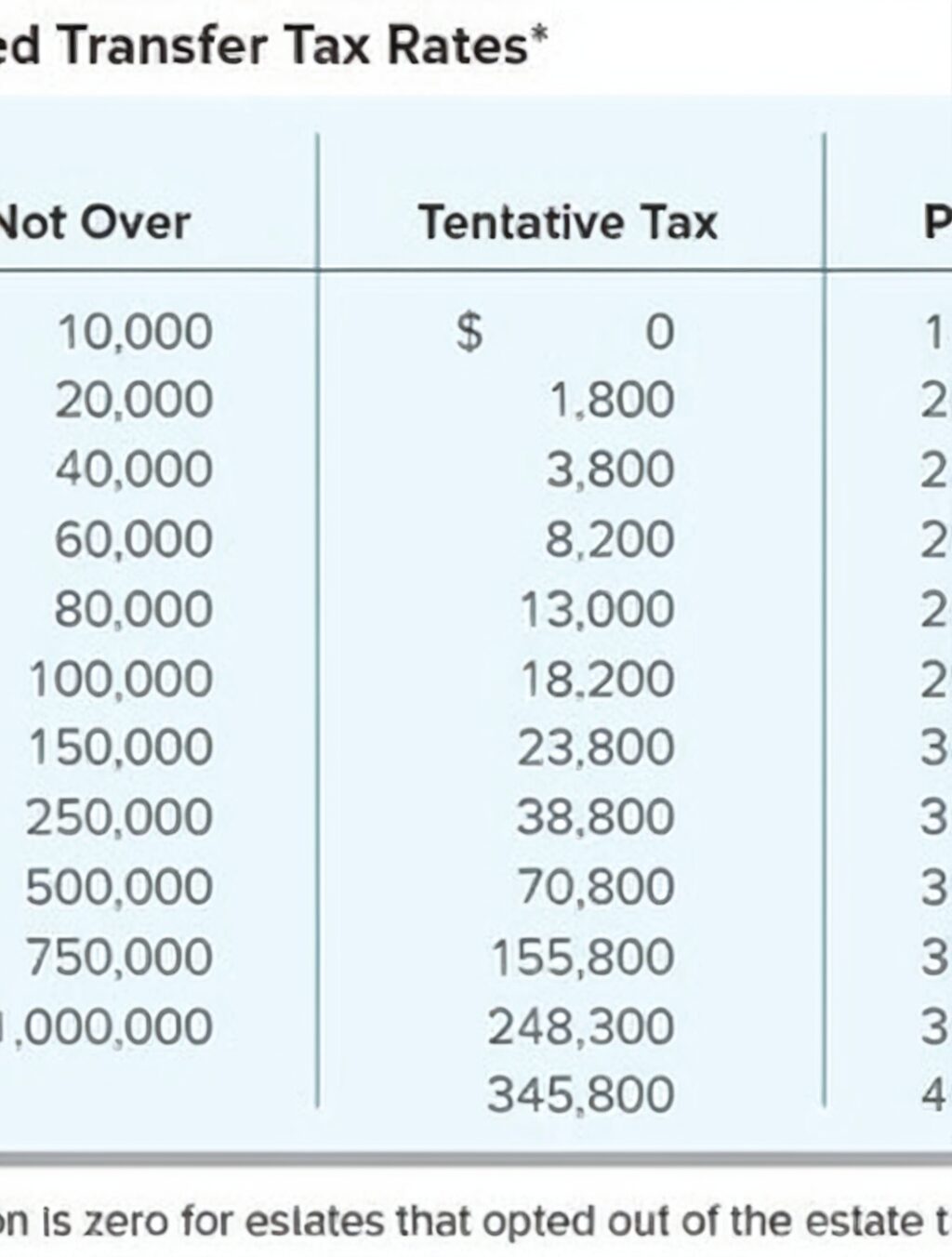
The gift tax rate is a progressive tax, which means that the rate increases as the value of the gift increases. The rates for 2023 are as follows:
- 18% for gifts over $10 million
- 16% for gifts over $5 million but not over $10 million
- 12% for gifts over $2 million but not over $5 million
- 8% for gifts over $1 million but not over $2 million
- 4% for gifts over $0 but not over $1 million
What is the Gift Tax Annual Exclusion?
The gift tax annual exclusion is the amount of money that you can give to someone each year without having to pay gift tax. The annual exclusion for 2023 is $16,000.
What are the Gift Tax Exemptions?
There are a number of exemptions to the gift tax, including:
- Gifts to spouses
- Gifts to charities
- Gifts for medical or educational expenses
- Gifts to political organizations
Gift Tax and 529 Plans
529 plans are tax-advantaged savings plans that can be used to pay for college expenses. Contributions to a 529 plan are not subject to gift tax, and earnings on the account grow tax-free. Withdrawals from a 529 plan are also tax-free, provided that the funds are used to pay for qualified education expenses.
Gift Tax and Inheritance Tax
Gift tax and inheritance tax are two separate taxes that are imposed on the transfer of property. Gift tax is imposed on gifts made during the donor’s lifetime, while inheritance tax is imposed on property that is transferred at death.
Gift Tax Annual Exclusion History
The gift tax annual exclusion has been in place since 1932. The amount of the exclusion has changed over the years, but it has generally increased over time.
Conclusion
Gift tax is a complex topic. If you are planning to give or receive a gift, it is important to consult with a tax advisor to ensure that you comply with the law.
FAQs about Gift Tax
- Q: What is the gift tax reporting deadline?
A: The gift tax return must be filed by April 15th of the year following the year in which the gift was received. - Q: Can I avoid paying gift tax?
A: There are a number of ways to avoid paying gift tax, such as making gifts within the annual exclusion limits or using a gift trust. - Q: What are the penalties for not paying gift tax?
A: The penalties for not paying gift tax can be severe, including fines and imprisonment.