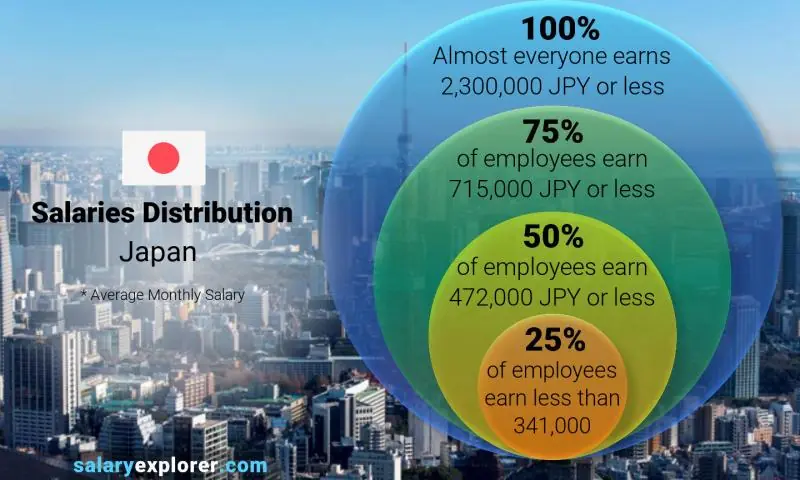
Navigating the complexities of the average salary in Japan can be challenging, especially when considering the numerous factors that influence earning potential. From regional disparities to industry-specific wages and the impact of experience, understanding these components is crucial for both job seekers and employers. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the different aspects that shape salary structures in Japan, providing valuable insights and future trends to help you make informed decisions about your career and financial planning.
Comparison of Salaries Across Different Prefectures
When discussing the average salary in Japan, it’s crucial to recognize substantial differences across various prefectures. These disparities arise from factors like local cost of living, industry presence, and economic activity.
Tokyo unsurprisingly stands at the top with the highest average salary, given its role as Japan’s economic hub. The bustling metropolis offers numerous high-paying jobs across finance, IT, and media sectors.
Conversely, Okinawa exhibits lower average salary figures. Its economy heavily relies on tourism, which generally offers lower wages compared to major industrial sectors.
Here’s a quick comparison table highlighting average salaries in selected prefectures:
| Prefecture | Average Annual Salary (JPY) |
|---|---|
| Tokyo | 6,200,000 |
| Osaka | 5,800,000 |
| Aichi | 5,700,000 |
| Fukuoka | 5,000,000 |
| Okinawa | 4,200,000 |
Several factors contribute to these variations:
- Economic Activity: Prefectures with a concentration of high-tech industries or corporate headquarters tend to offer higher salaries.
- Living Costs: Regions with higher living costs also tend to have higher salaries to offset these expenses.
- Population Density: Urban areas typically provide more job opportunities and higher wages than rural regions.
Understanding these differences helps job seekers make informed decisions. For example, if you’re seeking higher wages, Tokyo and Osaka might be ideal destinations. Conversely, those valuing a balanced lifestyle might consider prefectures with lower living costs but manageable salary levels.
In conclusion, while the average salary in Japan varies significantly by prefecture, aligning career goals with regional strengths can lead to optimal job satisfaction and financial well-being.
Breakdown by Industry: Who Earns the Most?
When examining the average salary in Japan, it is crucial to analyze how different industries impact earning potential. The Japanese job market demonstrates significant disparities in salaries across various sectors.
Here’s a closer look at which industries offer the highest salaries:
1. Finance and Insurance:
- Average Salary: ¥7,500,000 per year
- Jobs in finance, banking, and insurance often command higher wages due to the complexity and importance of the financial sector.
2. Information Technology:
- Average Salary: ¥6,800,000 per year
- The technology industry is booming. Both software engineers and IT specialists benefit from the high demand for tech skills.
3. Real Estate:
- Average Salary: ¥6,500,000 per year
- Real estate professionals, including brokers and property managers, enjoy substantial incomes driven by Japan’s ongoing urban development.
4. Manufacturing:
- Average Salary: ¥5,900,000 per year
- The manufacturing sector, particularly in automotive and electronics, provides solid earnings for engineers and skilled technicians.
5. Healthcare:
- Average Salary: ¥5,500,000 per year
- Medical professionals, such as doctors and specialized nurses, earn competitive salaries due to the essential nature of their services.
6. Education:
- Average Salary: ¥4,500,000 per year
- While not as high as other industries, educators, particularly at universities, receive respectable compensation for their roles.
Industry Salary Comparison:
| Industry | Average Salary (¥) |
|---|---|
| Finance & Insurance | 7,500,000 |
| Information Technology | 6,800,000 |
| Real Estate | 6,500,000 |
| Manufacturing | 5,900,000 |
| Healthcare | 5,500,000 |
| Education | 4,500,000 |
Hence, while considering the average salary in Japan, aligning career choices with these high-earning industries can significantly impact overall earnings. This insight proves crucial for professionals aiming to maximize their income potential.
The Impact of Experience on Salary Levels
Experience significantly influences the average salary in Japan. Generally, the more years of experience an employee has, the higher their salary tends to be. This trend reflects both the accumulation of skills and increased value that experienced employees bring to their organizations.
Typically, the salary progression looks like this:
- Entry-level (0-5 years): Most professionals in their early careers start with relatively modest salaries. However, they can expect steady increases with each year of experience.
- Mid-level (5-10 years): Salaries see a noticeable uptick as individuals enter mid-level positions. Employers value the blend of practical experience and growing expertise.
- Senior-level (10+ years): At this stage, professionals command the highest salaries. Senior employees often occupy leadership roles, providing critical insights and guidance.
To illustrate, let’s consider some average salary figures (in JPY) by years of experience:
| Years of Experience | Average Salary in Japan |
|---|---|
| 0-5 | ¥3,000,000 – ¥4,500,000 |
| 5-10 | ¥5,000,000 – ¥7,000,000 |
| 10+ | ¥8,000,000 – ¥10,000,000 |
Key Takeaways:
- Early Career: Focus on gaining diverse experiences and skill sets.
- Mid Career: Leverage expertise for higher positions and pay.
- Senior Career: Aim for roles that utilize extensive experience for maximum earning potential.
Understanding these trends can help job seekers and professionals strategize their career paths to maximize their average salary in Japan. By continuously enhancing their skills and experiences, individuals can effectively increase their earning potential over time.
Gender Pay Gap in Japan
The gender pay gap in Japan remains a significant issue despite recent efforts towards achieving workplace equality. Understanding the differences in the average salary in Japan between men and women can provide insight into this pressing topic.
Several factors contribute to the gender pay gap:
- Traditional Gender Roles: Historically, men have been the primary earners. Cultural norms still influence career choices and workplace behaviors.
- Career Interruptions: Women are more likely to take career breaks for child-rearing or elder care, impacting their long-term earnings.
- Industry Segregation: Commonly, men dominate high-paying industries such as finance and technology, while women often work in lower-paying sectors like retail and clerical jobs.
When examining the data on average salaries, a disparity is evident. Here’s a comparison to illustrate:
| Category | Average Salary (Men) | Average Salary (Women) |
|---|---|---|
| General workforce | ¥5,000,000 | ¥3,500,000 |
| Management positions | ¥8,000,000 | ¥5,500,000 |
| Part-time employees | ¥1,200,000 | ¥900,000 |
Key Observations:
- Women earn approximately 70% of what men make in similar roles.
- In management positions, the gap widens significantly.
- Part-time female employees earn roughly 75% of their male counterparts’ wages.
Addressing the gender pay gap involves systemic changes, including promoting equal opportunities, supporting career advancement for women, and ensuring pay transparency. Understanding these disparities in the average salary in Japan is crucial for fostering a more equitable workforce.